The dying days of a year are traditionally the time when Russia and China launch a number of payloads into orbit while Western nations are distracted as they celebrate their Christmas festival. And this year was no exception.
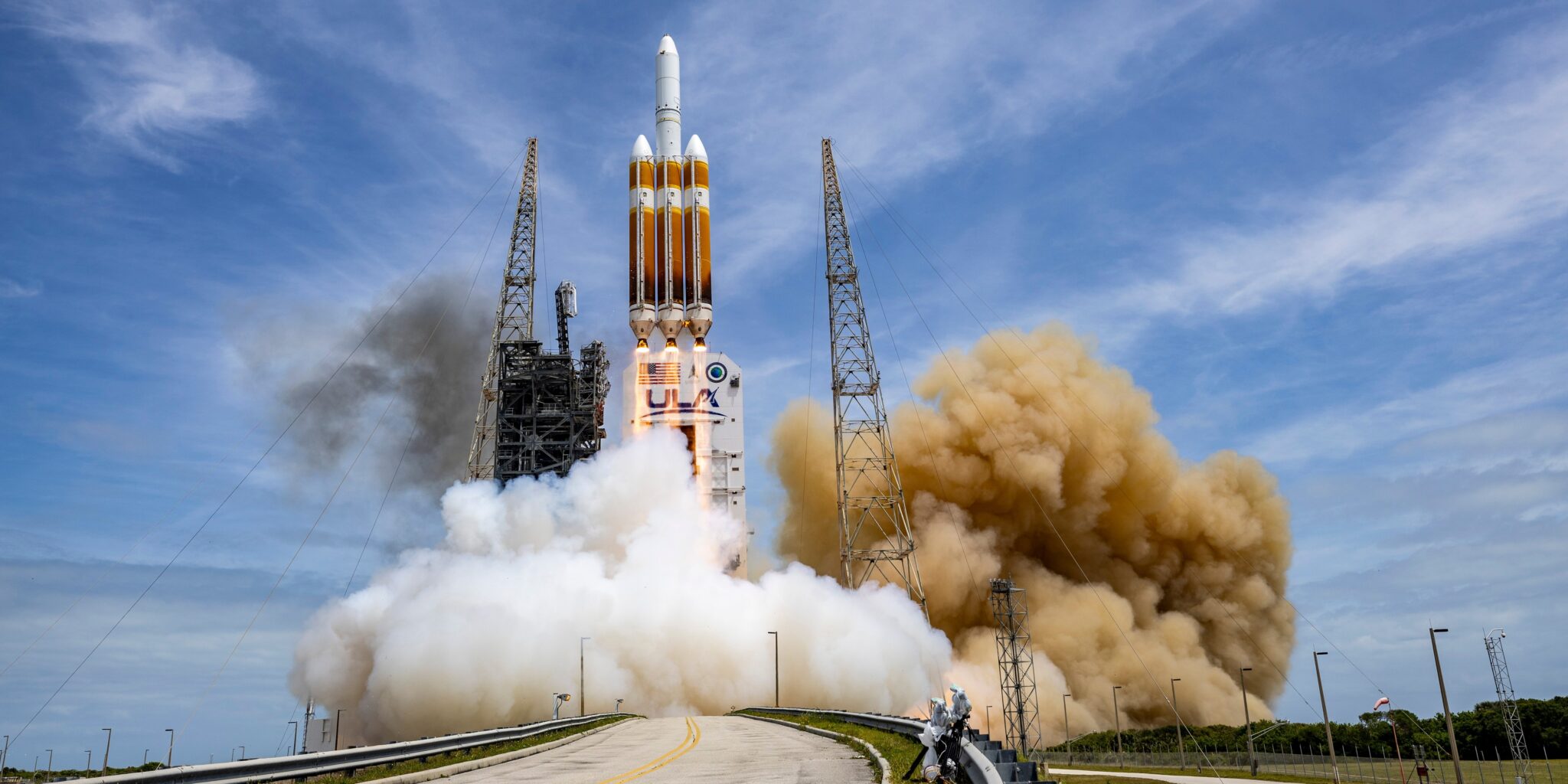
On 23 December at 0557 GMT from the Plesetsk launch site in Northern Russia, Russia made its first orbital attempt with its new Angara A5.1L launch vehicle. The flight carried a two metric ton dummy payload, dubbed GVM, into orbit. It was not intended to separate from the rest of the vehicle. While Russia had a successful suborbital test flight of the smaller Angara 1.2PP earlier in the year, this was the first fully orbital attempt of the more capable Angara A5 series.
The rocket, which is part of the family intended to eventually replace the Proton launch vehicle during the 2020s, uses the more powerful and less poisonous fuel combination of LOx/Kerosene. The main rocket consists of four RD-191 powered strap-on “first” stages, attached to a core “second” stage also powered by an RD-191. Atop sits a “third” stage powered by an RD-124A engine. Finally, like Proton, the rocket has a Breeze-M (Briz-M) upper stage.
Once a parking orbit had been reached, the Breeze M made further burns to attain a GTO (Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit) ) – the first achieved from the Plesetsk launch site – while also reducing the inclination. The Breeze M later placed the entire assembly into a graveyard orbit.
At 0301 GMT on 25 December 2014, Christmas Day according to Western religious calendars, Russia launched a satellite expected to be called Cosmos 2503 into a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) using a Soyuz 2-1b launch vehicle flying from Plesetsk. The spacecraft is believed to be a LOTOS-S used for Signals Intelligence gathering and was built by TSSKB Progress.
On 26 December 2014 at 1855 GMT the Russian Space Agency, Roscosmos, launched the Resurs P2 remote sensing spacecraft, again using a Soyuz 2-1b launch vehicle, but this time flying from the Baikonur Cosmodrome located near Tyuratam in Kazakhstan. The spacecraft, which is also built by TSSKB Progress, carries four imaging sensors, the best of which has a panchromatic resolution of 1m. In addition the spacecraft is carrying the NUKLON high energy particle detector experiment and an AIS receiver for the tracking of ships.
China launched a high resolution Earth observation satellite called Yaogan 26 at 0322 GMT on 27 December 2014 using a Long March 4B flying from Taiyuan. The spacecraft is believed to have been built by CAST.
Proton may eventually be replaced in the 2020s by the Angara series but for the time being it remains the mainstay of commercial launch provider ILS. A Proton M/Breeze M, operating under ILS colours, successfully launched the Airbus-built Astra 2G commercial communications spacecraft for SES. The launch occurred from the Baikonur Cosmodrome near Tyuratam, Kazakhstan. The 6,002kg Eurostar-3000 bus design satellite was successfully put into a GTO from where it used its own on-board engine to achieve a full GEO (Geostationary Earth Orbit) position.
The final and 92nd orbital flight attempt of the year (a 20-year high) occurred at 0102 GMT on 31 December 2014 when a Long March 3A successfully lifted off from Xichang, China, carrying the Chinese Feng Yun 2G weather satellite. The 1,369kg spacecraft was built by Shanghai Institute of Satellite Engineering (Part of SAST). The spacecraft was initially injected into a transfer orbit but will use a solid rocket apogee kick motor to circularise itself into a full GEO.