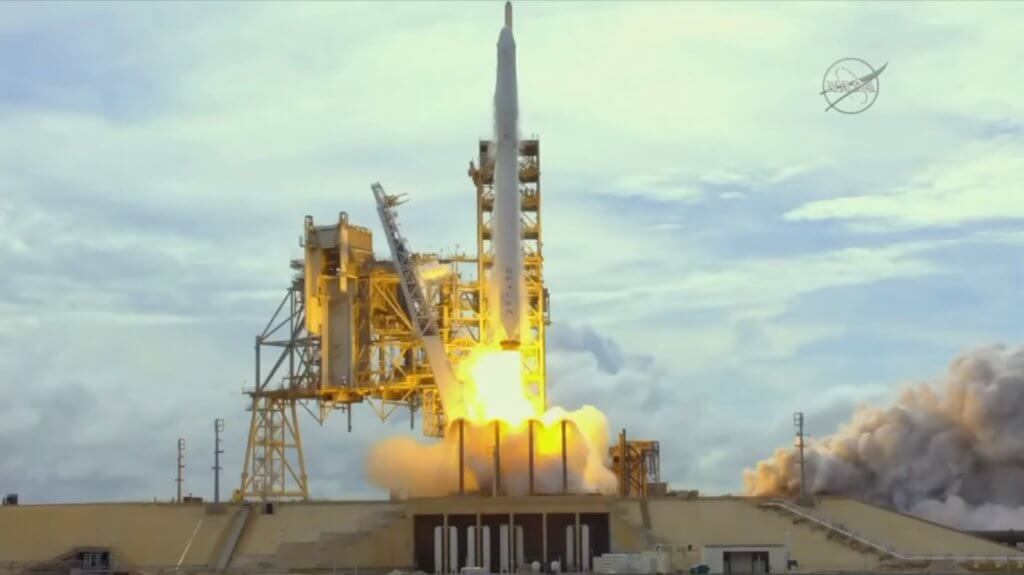
Launch pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center celebrated its 100th launch on 3 June when a SpaceX Falcon 9v1.2FT-R took off carrying the CRS-11 resupply mission to the ISS (International Space Station). The launch had been delayed by two days due to thunderstorms in the vicinity of the launch site. The launch occurred at 2108 GMT, and was followed by a landing of the newly built but reusable Falcon 9 first-stage seven minutes and 27 seconds later at the Landing Zone 1 site at Cape Canaveral – a feat that is rapidly becoming mundane. The launch was further notable as it marked the first reuse of a previously flown Dragon capsule. The capsule, known as C106 to its manufacturers, was first flown in September 2014 on the Dragon CRS-4 mission.
This re-use of a Dragon capsule is just another step along the quest to total reusability that Elon Musk and SpaceX seems to be forging down. For this initial example of capsule reuse, some parts have had to be changed/refurbished. Most obvious is a new heat shield for the craft along with some more minor battery changes due to exposure to sea water after its previous splashdown. The capsule’s thruster system is an example of a major component that remains largely untouched since the last flight, having been deemed flight worthy after evaluation by both SpaceX and NASA teams. SpaceX worked closely with NASA to gain approval for reuse of the capsule. While already flown on a commercial mission, the use of a “flight proven” rocket on a NASA mission is still in the works.
The SpaceX Dragon CRS-11 mission carried 2,708 kg of cargo to the ISS. Of this 1,002 kg is made up of three experiments carried as “Unpressurised Cargo” held in the capsule’s trunk. These experiments are; ROSA (Roll-Out Solar Array) for USAF Research Laboratory, NICER (Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer) for NASA and MUSES (Multiple User System for Earth Sensing) developed by Teledyne Brown. Alongside, these payloads the Dragon also carried five 1U cubesats forming the Joint Global Multi-Nation Birds Satellite project (BIRDS 1) headed by the Japanese Kyushu Institute of Technology (KIT) and involving several non-spacefaring nations.
Update: Due to the unexpected two day delay to the Dragon launch schedule, NASA made the decision to move the planned unberthing of the resident Orbital ATK Cygnus OA-7 craft up from 16 July to earlier in the month. The Cygnus craft was released by the robotic Canadarm 2 at 1310 GMT, 4 June, over the South Atlantic.
Cygnus OA-7 spent week conducting the on-board SAFFIRE 3 low-gravity fire experiment and deploying four LEMUR-2 cubesats for Spire Inc. It was deorbited to re-enter the atmosphere to burn up on 11 June.
Further Update: Following a 41-hour rendezvous with the ISS, the SpaceX Dragon CRS-11 craft was acquired by Canadarm 2 at 1452 GMT on 5 June and berthed on the Harmony module at 1610 GMT (all times from Jonathan McDowell).