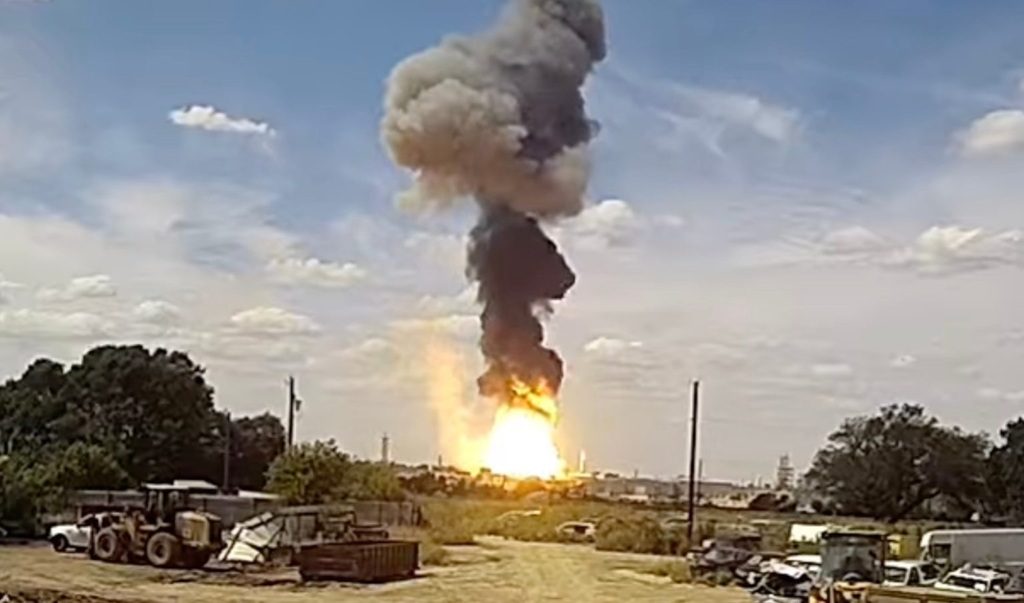
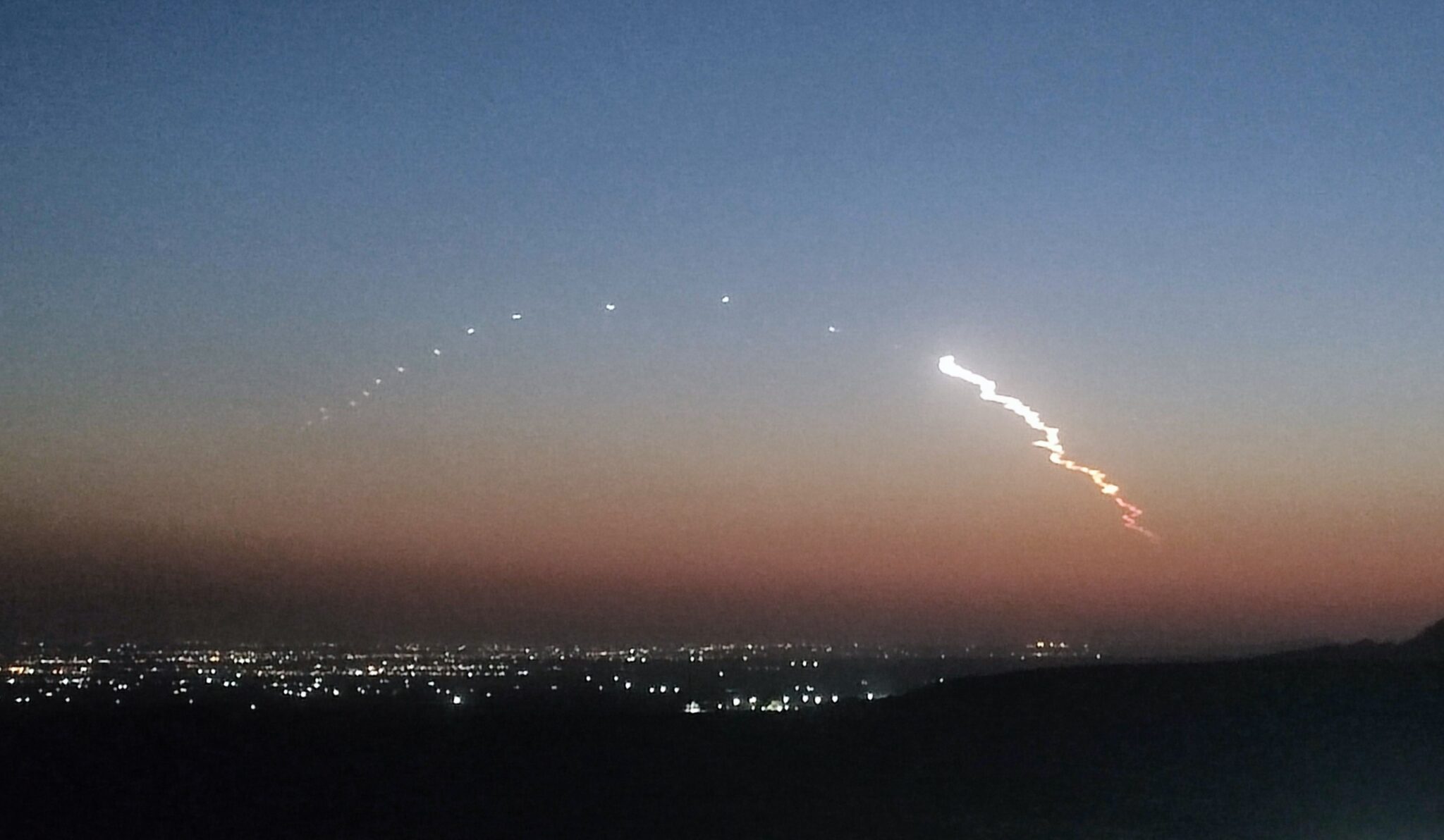
Astra Space has released its investigation findings into the Astra Rocket 3.3 launch failure which lost a pair of NASA’s TROPICS-1 mission satellites. The TROPICS-1 mission launched on 12 June 2022 on Astra’s Rocket 3.3, serial number LV0010. The rocket completed a nominal first stage flight, stage separation, and upper stage ignition. Shortly after the ignition of the upper stage engine, the upper stage’s fuel consumption rate increased and remained anomalously high for the remainder of the flight. About 250 seconds after upper stage ignition, the stage exhausted its fuel supply with approximately 20% of the liquid oxygen still remaining onboard. As a result, the upper stage was only able to obtain about 80% of the required orbital velocity. The stage was unable to deliver its payloads to orbit, and subsequently re-entered the atmosphere, ending the mission.

Astra Rocket 3.3 launch went initially well but its second stage later shutdown early losing two NASA TROPICS satellites. Courtesy: NASASpaceflight/Astra Space Inc
The investigation’s analysis showed that the anomalous fuel consumption during the pressure-fed upper stage engine burn was due to a combustion chamber wall burn-through that occurred 18 seconds into upper stage flight. Flight data showed that the burn-through in the Aether engine was precipitated by a substantial blockage of the fuel injector. The blockage was probably caused by gaseous fuel in turn caused by its boiling. The result of the burn through is that some fuel flow is directly into the combustion chamber, essentially wasting it.
A major factor was that there was not enough thermal barrier coating on the suspected burn through area. This has not been correctly modelled relative to the altitude of operation and led to an incorrect design assumption. Testing only on the ground meant that the exhaust is not fully attached to the wall of the nozzle, heating it less, implying less coating was needed. Whereas, at the altitude where the failure occurred where there is less atmospheric pressure, thus the exhaust was fully attached to the nozzle wall, resulting in more heating and hence resulting in gaseous boiling. It was also noted that slightly higher meteorological temperatures on that day made boiling more likely. Other factors included using a pressure-fed upper stage engine that operates at relatively low pressures, making boiling more likely, as well as the selection of a kerosene-like fuel with a higher vapor pressure than traditional rocket-grade kerosene (e.g. RP-1).
Astra has since elected not to pursue the Astra Rocket 3 and has moved onto a new Astra Rocket 4 design, incorporating the lessons it has learned from this failure.
The full results of the failure report are here:
Conclusion Of TROPICS-1 Mishap Investigation | Astra