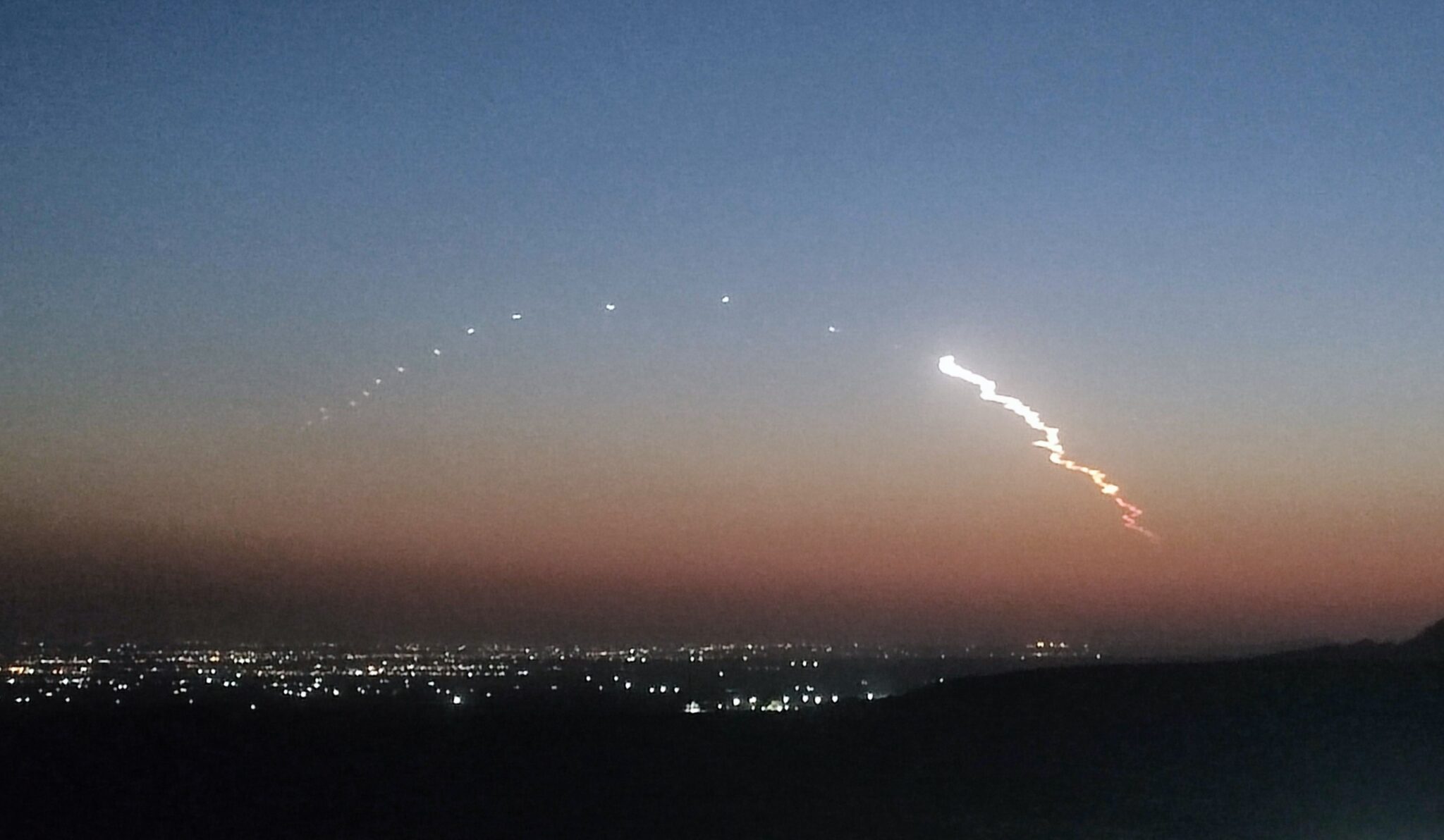
The Japanese meteorological satellite, Himawari 8, as successfully launched by a H-IIA (H-2A202) launch vehicle from the Tanegashima launch site in Japan at 0516 GMT on 7 October.2014. The spacecraft which was built for JAXA by the Mitsubishi Electric Corp (MELCO), uses a version of its DS-2000 bus. The spacecraft will operate from the 140 degree East position in Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO).
The satellite carries Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI), Space Environment Data Acquisition Monitor (SEDA) and the Data Collection Subsystem (DCS). The Advanced Himawari Imager is the spacecraft’s main instrument. It can produce images at a resolution of up to 500 metres, with each spectral band being of use for different observations, allowing the satellite to collect data on various factors including cloud cover, temperatures, winds, precipitation and aerosol distribution. The Space Environmental Data Acquisition Monitor will collect space radiation data, studying protons and electrons incident upon the spacecraft. The Data Collection Subsystem is a communications payload which will be used to collect and relay data from ground weather stations for analysis.