The month of September 2022 saw a spate of small satellite orders (plus some shared rides) made. These included:
US Start-up Rogue Space Systems is planning a pair of satellites dubbed a cubesat-class spacecraft dubbed Space Robot to service and repair small satellites in orbit. It has signed with SAIC to help design and integrate these satellites which are due for launch in 2023. SAIC will help develop Rogue’s fleet of Orbital Robots for other duties including space situational awareness and assembly in orbit.
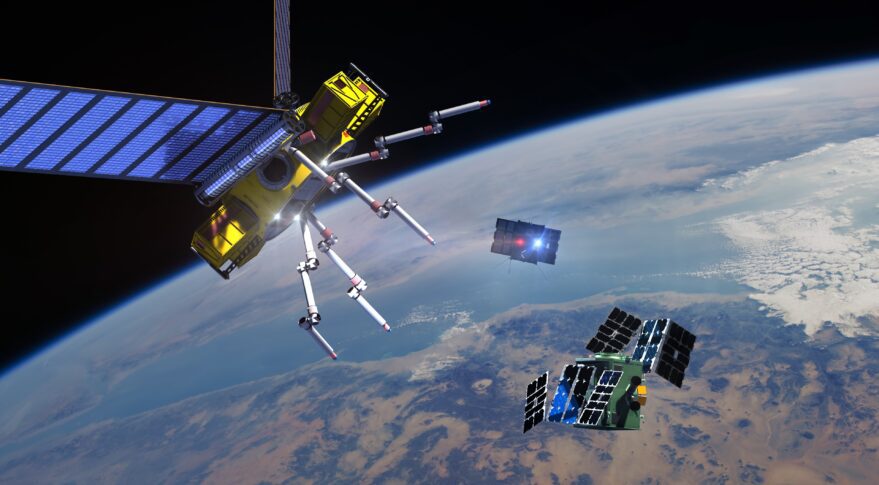

Artist’s impression of “wasp like” looking Orbital Robot repair and servicing spacecraft. Courtesy: Rogue Space Systems
Spire Global announced that it was building three 16U Cubesats to carry GHGSat greenhouse gas (especially methane) monitoring payloads. The satellites will be launched in late 2023. These three will add to the Montreal-based GHGSat’s growing satellite constellation of six UTIAS (University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies) Space Flight Laboratory-built satellites in low Earth orbit already with a further three already on order to be launched in early 2023.
Satlantis, a Spanish Earth-observation technology company, has ordered two 100-150 kg class multispectral satellites from OHB Sweden using OHB’s InnoSat platform/bus design. Satlantis is to supply the camera payload able to take optical and infrared imagery with a resolution of 0.8m per pixel. The satellites are expected to weigh less than 150 kilograms and launch in 2024. Again, a major application for the satellites will be methane detection.
In a separate development involving Satlantis, was the announcement that it would be working with the Finnish Iceye firm to launch a set of four satellites – two optical and two synthetic aperture radar types as the Tandem4EO constellation. The idea is that the two radar satellites would be in a bistatic formation allowing interferometry depth/height measurement applications supported by two following sub-1m resolution optical satellites in the same orbit providing imagery of less than 1 m per pixel.
In respect to rides to space – or rather to the Moon – the United Arab Emirates (UAE) announced that, under a Memorandum of Understanding with China, its developed by the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Center (MBRSC) built Rashid 2 lunar rover would be taking a ride to the lunar South Pole’s surface on the back of a Long March 5-launched Chang’e 7 lunar lander mission in 2026. China’s Chang’e 7 will also carry a follow-on to China’s Yutu lunar rover series. Rashid 2 is itself a follow-on to Rashid 1 rover which is due to the launched to the Moon on board a Falcon 9-launched a Japanese I-Space M1/Hakuto-R lander next year.
ESA (via its ARTES and Horizon Europe programmes) has formally begun its project for a Eagle-1 satellite to test out QKD (Quantum Key Distribution) secure ground communications via this transmitted key technology with an initial contract being given to a consortium of 20 companies led by the European satellite operator SES. The spacecraft is designed to have a mission life of three years in low Earth orbit. The satellite is taken as Europe’s attempt to catch up with China’s and Singapore’s QKD research effort as well as that done by the UK-based Arqit firm. Singaporean firm SpeQtral is planning to deploy its first QKD research satellite in 2024.