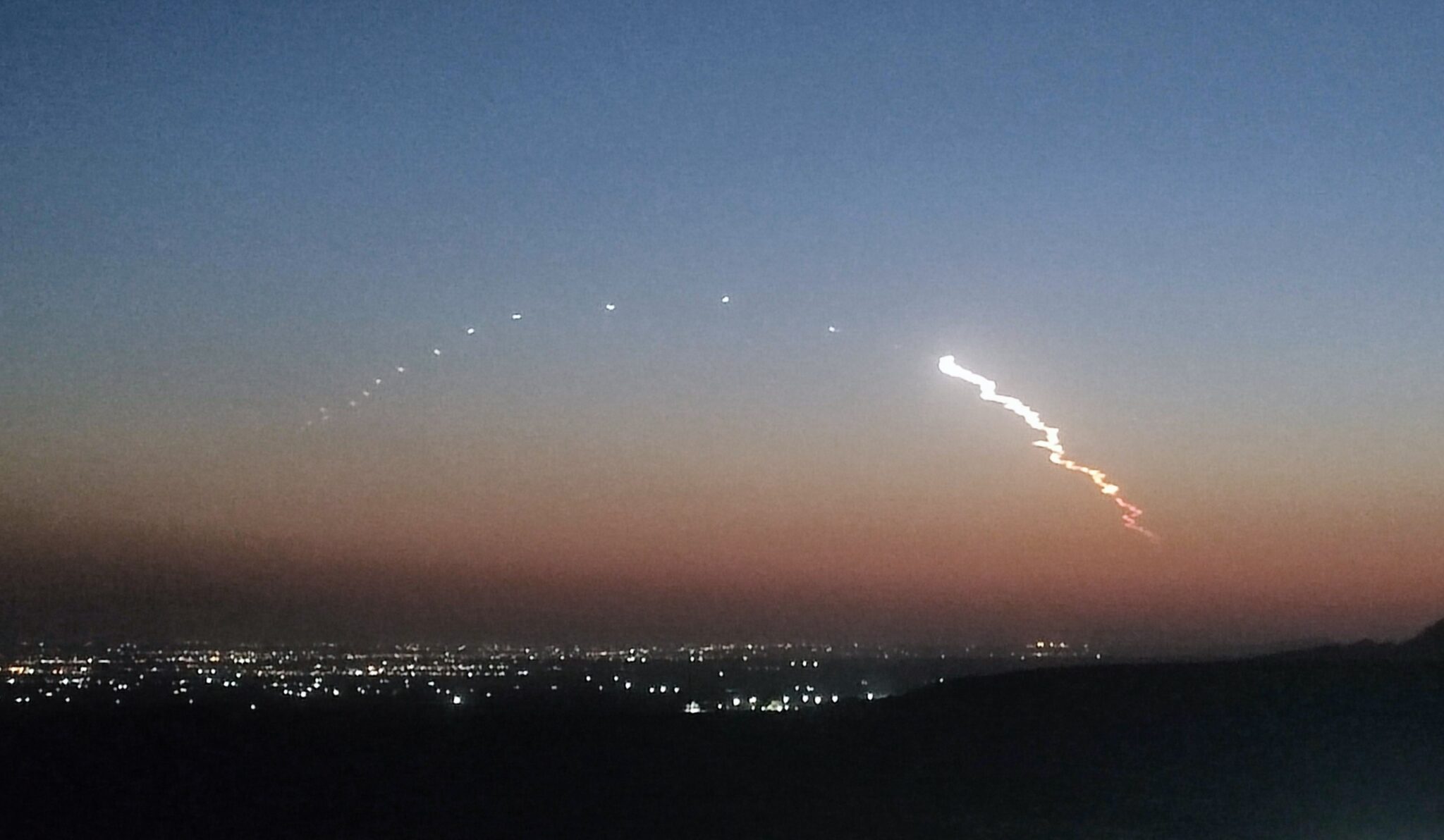
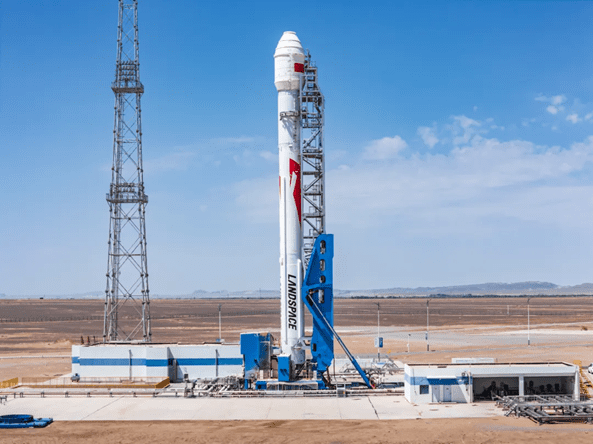
At 0943 GMT on 29 June, a previously flown SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifted-off from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and for its First stage for the second time. The First stage flew for the first time in April carrying the NASA TESS telescope. This time it carried the SpaceX DRAGON CRS-15 cargo ship, on another trip bound for the International Space Station (ISS). The DRAGON capsule – serial number C111 – was previously used for the CRS-09 mission in July 2016.
The whole rocket stack was in a Block 4/5 configuration, meaning it used a older Block 4 First stage with a new Block 5 Upper stage on top. The Block 5 units represent the final major iteration of the Falcon 9, with their associated First stages designed to be flown 10-times – as opposed to only twice for the Block 4s. And this may well be the last time we see the older Block 4 First stages, since SpaceX is now ready to roll-out its final iteration Falcon 9 Block 5s. The next two launches in their manifest for the seventh IRIDIUM NEXT mission and TELSTAR 19 VANTAGE are confirmed to be using full Block 5 rockets. The full Block 5 made its debut in early May launching the BANGABANDHU-1 satellite.
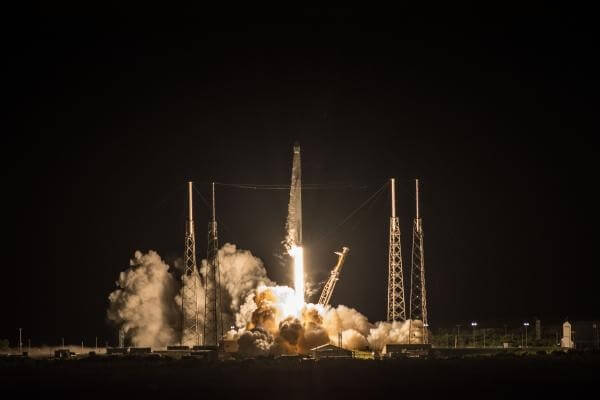

The Falcon 9 rocket lifts-off from Cape Canaveral carrying the CRS-15 mission. Courtesy of SpaceX
The DRAGON capsule is carrying 2,700 kg of equipment, experiments and supplies to the ISS. The main experiment being carried in the capsule’s trunk is the NASA ECOSTRESS (Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment) payload which will be mounted onto the outside of the ISS, and will monitor the temperature of Earth’s plant life.
Riding inside the DRAGON capsule are six CubeSats: three Biarri-Squad, 3U-CubeSats from Project Biarri testing precision flying techniques and risk mitigation; and another three 1U-CubeSats from the BIRDS Project representing the Bhutan Ministry of Information and Communications (BIRD BTN), the University of the Philippines (BIRD PHL) and University Technology MARA (BIRD MYS). These units will be taken onboard the ISS and deployed form the Japanese Kibo module at a later date.
Update on 3 July: The DRAGON CRS-15 cargo craft was grappled by the ISS robot arm at 1054 GMT on 2 July.