For the third consecutive month, SpaceX has brought launches of its Falcon 9 rocket to a temporary halt after an anomaly occurred on its latest crewed mission.
What happened?
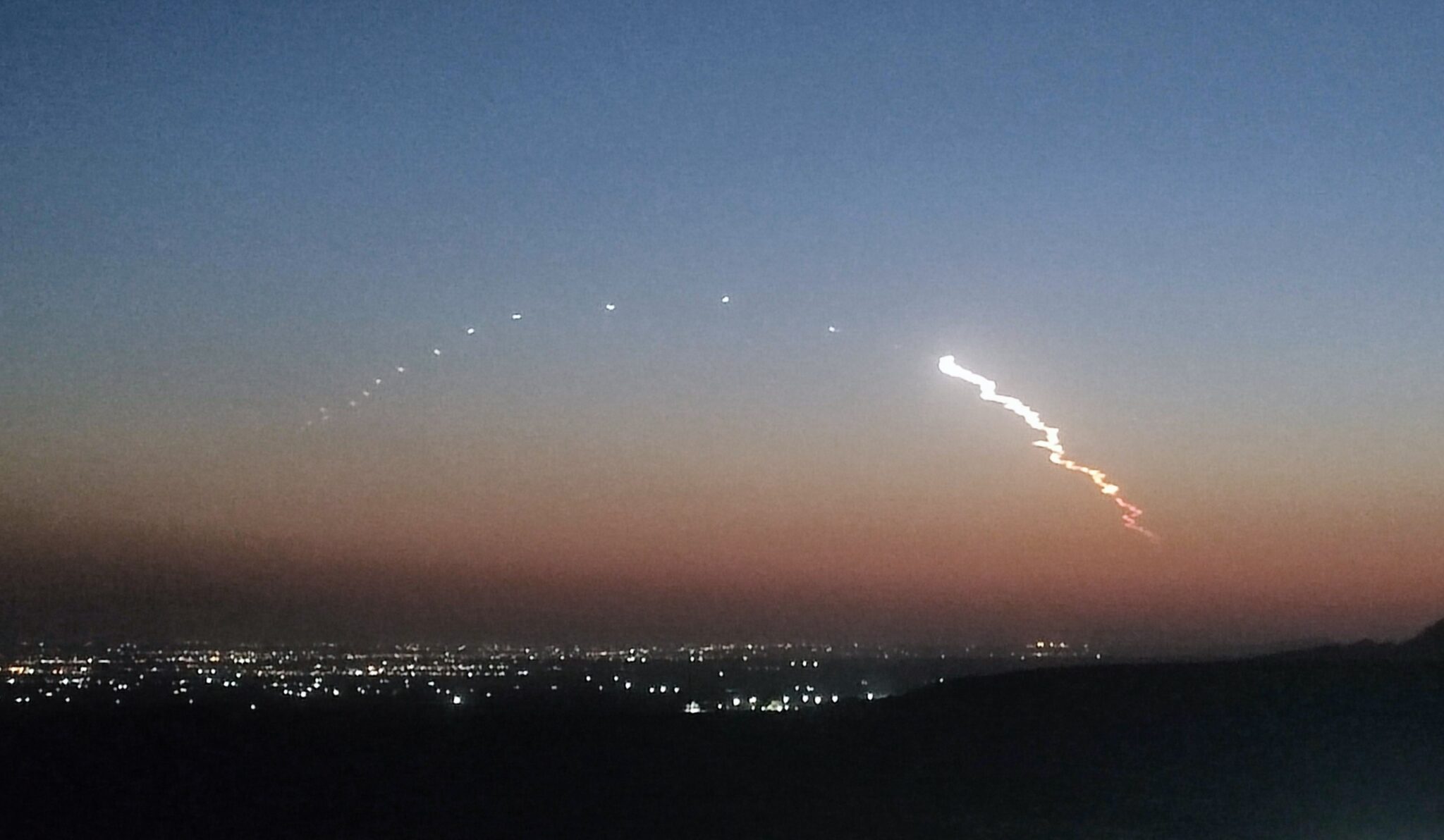
Crew-9 was launched aboard a Falcon 9v1.2FT Block 5 at 17:17 (GMT) on 28 September from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, US. The rocket carried and placed Freedom, a Crew Dragon spacecraft, into orbit.
The point of the mission was to carry NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Russian cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov to the International Space Station (ISS), where they will spend the next five months conducting research as part of Expedition 72. The astronauts safely reached their destination on 29 September. In theory, everything went well.
However, on the same day Crew-9 reached the ISS, SpaceX revealed that the upper stage of its launch vehicle “experienced an off-nominal deorbit burn” during its journey. The upper stage returned safely to the ocean but the anomaly it suffered meant that its landing fell “outside of the targeted area” which was in the east of New Zealand.
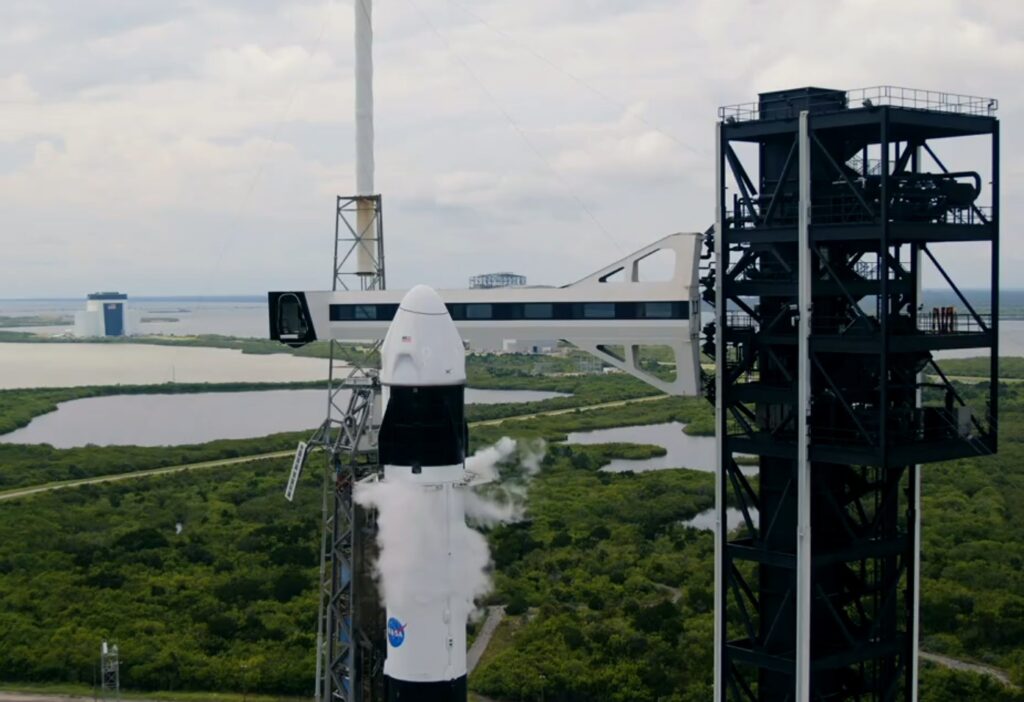

The Crew-9 mission prepare for lift-off on a Falcon 9 rocket, the upper stage of which later experienced an anomaly. Courtesy: SpaceX
A targeted re-entry of a rocket’s upper stage is important to ensure that it does not fall on a populated area and to avoid having to abandon it in orbit, adding to the growing mound of orbital debris in space.
SpaceX did not provide further information but announced that all its Falcon 9 launches would be halted while the company investigated the incident further.
It is the third time since January that the launch behemoth has grounded its workhorse rocket, and the second time in less than three months that a problem with the upper stage has been identified.
In July, a routine launch went awry after a liquid oxygen leak on the upper stage developed within the insulation around the upper-stage engine during the first burn of the second-stage engine. A second burn was planned to circularise the orbit ahead of satellite deployment. However, the initial leak led to the excessive cooling of engine components, most importantly those associated with delivery of ignition fluid to the engine. As a consequence, the engine experienced a hard start, rather than a controlled burn, that damaged the engine hardware and caused the upper stage to lose attitude control. The 20 satellites aboard were deployed but in lower orbits than planned, with most quickly re-entering.
Comment by Farah Ghouri: It is hard to ignore the irony of a rescue mission (no matter what NASA prefers to call it) suffering its own problems en route to picking up a pair of otherwise stranded astronauts.
Crew-9 originally consisted of four astronauts but NASA removed Zena Cardman (who would have been commander) and Stephanie Wilson from the flight to create space for NASA astronauts Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore to, finally, return to Earth when the Crew-9 mission wraps up in early 2025. Williams and Wilmore flew to the ISS on Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner in June, intending to stay for around one week. After NASA decided that Starliner would return uncrewed, they were basically stranded (in fairness, the agency had already come up with the Crew-9 return plan).